We are able to see so many things around us and this possible only due to the presence of light. Suppose if we get into a dark room with no light at all, we cannot see anything around us. But in the same place is we turn on the light or light a candle we can see the things and objects present inside that room. Hence without light things cannot be seen, light helps us to see objects.
The Sun gives its own light and during the day, its light allows us to see objects. Such objects like the sun that give out or emit light of their own are called luminous objects.
Depending on the light transmission capacity, objects can be of different types. If we cannot see through an object at all, it is an opaque object. If you are able to see clearly through an object, it is allowing light to pass through it and is transparent. There are some objects through which we can see, but not very clearly. Such objects are known as translucent.
Or in other words transparent objects allow all the light to pass through them, translucent ones allow partial light to pass, whereas opaque ones allow no light to pass through.
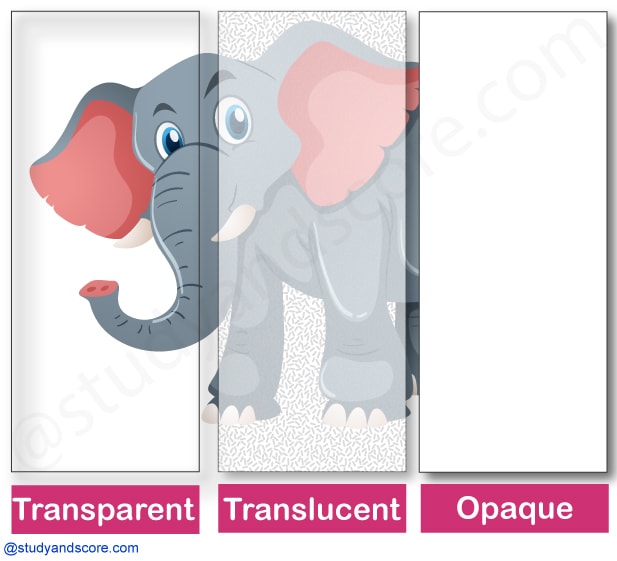
| Transparent objects | Translucent objects | Opaque objects |
|---|---|---|
| A material through which light can pass completely. | A material through which light can pass partially. | A material through which light cannot pass at all |
| We can see clearly through these objects. | We can see partly through these objects. | We cannot see through these objects |
| Also called as see-through objects (ST objects) | Also called as partially-see-through objects (PST objects) | Also called as non-see-through objects (NST objects) |
| The color of these objects depends on the amount of light they emit. | The color of these objects depends on the amount of light absorbed, scattered and reflected | The color of these objects depends on the amount of light they absorb. |
| We will be able to see the object lying on the other side of transparent objects. | To some extent we will be able to see the object lying on the other side of translucent objects. | We will not be able to see the object lying on other side of opaque objects. |
|
For example, Let us take an empty glass. It is a transparent object we can see through it. Light can completely pass through it. All the colors of the light spectrum are reflected by the glass. |
For example, Let us take a frosted window glass. It is a translucent object and we can barely see through it. Light can diffusely pass through it. The partially absorbed light scatters in different directions from a translucent glass. |
For example, Let us take an apple. It is an opaque object as we cannot see through it. No light can pass through an apple. All the colors of the light spectrum are absorbed by apple and red color is reflected back. |
| Other examples of transparent objects include computer screen, glass, fish aquarium, camera lens etc. | Other examples of translucent objects include wax paper, tracing paper, butter paper, colorful balloons etc. | Other examples of opaque objects include Cardboard, mobile phone, Wood, Metals etc. |
Everything around us (living or non-living) forms shadows. Shadows form due to the property of objects to block the light. Opaque objects do not allow any light to pass through them. The dark patch formed on the ground when an opaque object is held in the sunlight is called the shadow.

We need a source of light and an opaque object, to see a shadow. Shadow gives us some information about the object. These shadows can sometimes also mislead us about the shape of the object. We can create a few shadows with our hand and make believe that they are shadows of animals.
The size of the shadow changes depending on the angel of the light. Our shadow keeps changing throughout the day. It is longest in the early morning and the late afternoon. During afternoon, when the sun is overhead there is very little or no shadow at all. Because the position of sun changes throughout the day, the angle at which the rays fall on the ground also change
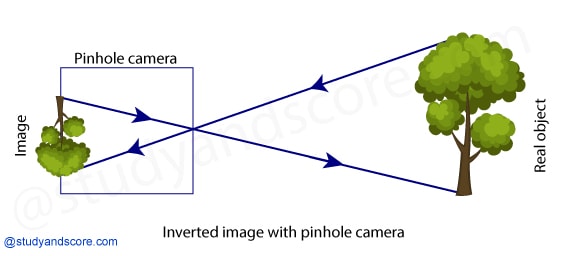
Pinhole camera is eleventh century Arabic invention. It was then used to view solar eclipse. During its initial invention, it was actually a dark room with a single small hole in the wall. Through this hole the light was admitted. Inside this room the outside scene was visible as an inverted image. Artists of that time used this pinhole camera as an aid to achieve correct angle in their drawings and paintings. Later in sixteenth century, Leonard da Vinci described this as Camera obscura. ‘Obscura’ is a Latin term meaning ‘dark room’.
You can look at some distant objects like a tree or a building or vehicles and people moving on the road through this pinhole camera. The objects you are trying to look must be in bright sunshine. Move the smaller box forward or backward till you get a picture on the tracing paper pasted at the other end.
You will be surprised to see that the image formed is inverted compared to the real object. This is because the light passing through the hole forms an inverted image of the external object on the opposite side of the box.
We can image the with our pinhole camera with slightly different setup. For this we need a large sheet of cardboard with a small pin hole in the middle. Hold the sheet up in the Sun and let its shadow fall on a clear area. We can see a small circular image of the Sun in the middle of the shadow of the cardboard sheet.
We can make use of this set up to view eclipse. We can observe a part of the Sun's image gradually becoming darker as the eclipse starts. Do remember, Never look directly at the Sun, it could be extremely harmful for the eyes.
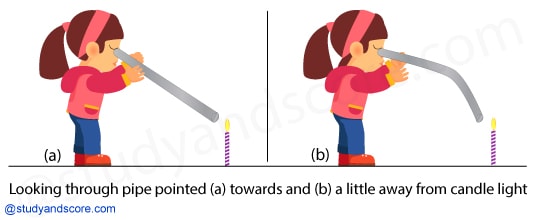
Light travels in straight lines and this is the reason that the opaque object obstructs the light forming a shadow behind. We can see the light of a fixed candle from a long pipe when the pipe is straight, but when the pipe is bent we cannot see the light of the candle.
When we look ourselves into the mirror we can see our own image. This is what is called as the reflection. We can see the reflections of all the objects which are in front of the mirror. Mirror reflection gives us clear images. Images are very different from shadows.

This activity suggests that a mirror changes the direction of light that falls on it. Hence we can say that light travelling along straight lines gets reflected from a mirror.
This activity gives us an idea of the manner in which light travels and gets reflected from a mirror.
Link to Solutions on this topic
- Share with your friends! -
Login to post your comment here...
- or with social Account -