Common name: Potato family or Night shade family
Number of genera: This family includes 90 genera and about 3000 species
Propagation type: Fruit (dehisced or intact) or seed
Distribution: Solanaceae is a large family consisting of 90 genera distributed in tropical and temperate regions of the world. They are mainly found in Central and South America. In India, this family is represented by 15 genera and 88 species. Most of the species are cultivated throughout India and a few are found in Himalayas, Southern and Eastern India.
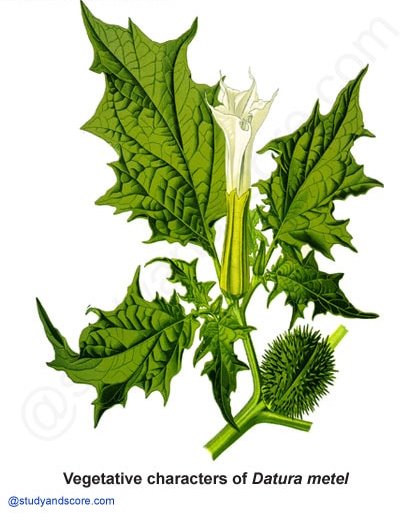
Habitat: Members of this family are mostly mesophytes and some are xerophytes (Solanum suratense).
Habit: The habit of the members of this family is variable. Some plants are annuals or perennial herbs (Solanum nigrum, Solanum surattense). Few plants are shrubs (Solanum torvum) and small trees (Solanum verbascifolium) and rarely climbers (Solanum dulcamara)
Root system: The members of this family have tap root system.
Stem: The stem is aerial, erect and mostly herbaceous. It is covered either by prickles (some species of Solanum) or spines (Lycium), spines are modified branches. In Solanum tuberosum the stem is an underground tuber. The petiole commonly shows adnation with the stem. Vascular bundles are bicollateral type. In bicollateral vascular bundles phloem is present on either side of the xylem, separated by cambia.
Leaf: Leaves are simple, entire, lobed, exstipulate and petiolate. Leaves show alternate or terminal phyllotaxy in the vegetative regions. And in the region of inflorescence, leaves appear to be opposite or whorled due to the fusion of petiole with the internode. They are usually simple or pinnately lobed. Venation is reticulate.
Inflorescence: It is usually cymose type. It may be terminal or axillary in position. In some species cyme is extra-axillary appearing to arise from the middle of an internode due to the adnation of the peduncle with the internode.
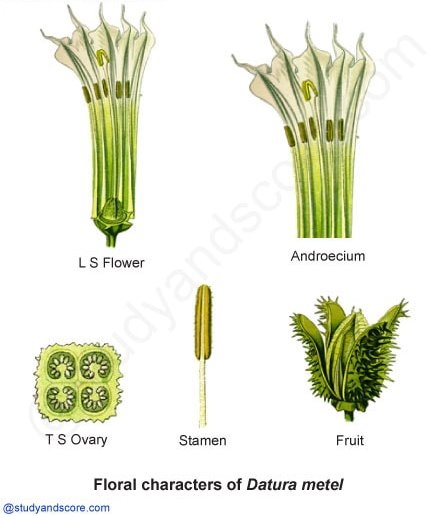
Flower: The flowers appear to be solitary and axillary as in Datura. Flowers are sometimes clustered as in Withania. The flowers are ebracteate, ebracteolate, pedicillate, actinomorphic or sometimes zygomorphic (Salpiglossis, Schizanthus), complete, bisexual (unisexual in Withania), pentamerous and hypogynous.
Calyx: The calyx consist of 5 sepals which are fused (gamosepalous). The aestivation is valvate. The calyx in some plants (Solanum) is persistent and much enlarged in fruit. The lobes of calyx are valvate in bud.
Corolla: The corolla consists of 5 petals. Corolla is gamopetalous and funnel-shaped (Datura), campanulate (physalis), rotate (Solanum). The aestivation is valvate or twisted. Sometimes the corolla is strongly zygomorphic and may become bi-lipped as in Schizanthus.
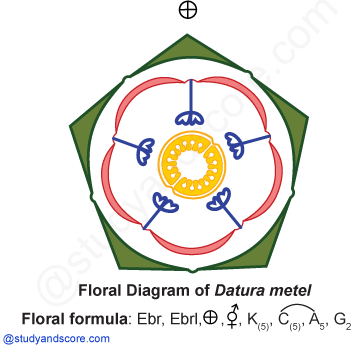
Androecium: Stamens are five in number, epipetalous on the corolla tube and alternate with the lobes. They are usually unequal in height. In some zygomorphic forms there are only four stamen (Salpiglossis) or two fertile stamen and remaining are staminodes (Schizanthus).
The anther lobes are large, ovate or oblong, dithecous, basifixed and introse. The dehiscence may be longitudinal (Datura) or apical pores (Solanum).
Gynoecium: Gynoecium consists of bicarpellary and syncarpous ovary which is oblique in position due to the tilting of posterior carpel to the right and anterior carpel to the left at an angle of 45o. The ovary is usually bilobular, occasionally unilocular (Capsicum). It becomes tetralocular due to the development of false septum in Datura.
There are numerous ovules arranged on axile placentation on swollen placenta. The style is linear, terminal and stigma is capitate or shortly lobed. A hypogynous nectariferous disc is usually present at the base of the ovary.
Pollination: Flowers are usually protandrous. Some species of Solanum are protogynous. Cross pollination through insects is common. Occasionally, self-pollination may occur in Nicotiana
Fruit: The fruit is mostly berry sometimes enclosed within an inflated bladder-like calyx (Physalis) or it is a capsule which dehisces by valves (Datura) or circumcised above the middle (Hyoscyamus). Fruit is Septifragal capsule in Datura and Nicotiana.
Seed: The seeds are numerous, compresses, discoid or suberniform, dicotyledonous, endospermic with curved or straight (Nicotiana) embryo.
Family solanaceae is also called as the potato family or the nightshade family. This family has more than 90 genera and around 3000 species. The members of this family are distributed throughout the world. Its members are characterized by flowers with five petals, sepals, and stamens and alternate leaves. Many of the species of this family contain toxic alkaloids. The following is a list of some important members of family Solanaceae, arranged alphabetically:
The family solanaceae contributes several important food, drug and ornamental plants to human race. Hence this family is considered as economically important.
Solanum species: Solanum tuberosum is most important food crop after cereals. These stem tubers which are rich in carbohydrates and sugars are prime food and are eaten cooked or baked. Apart from acting as food, potato is also a source of some industrial products like dextrin, syrup, starch and several other alcohols.
Solanum melongena is used as a vegetable. It is commonly cultivated in warm countries. It is known for its various shapes and color.
Several other Solanum species are climbers which are cultivated in gardens. For example: Solanum jasminoides (fragrant, white tinted blue flowers), Solanum dulcamara (violet spotted green flowers), Solanum seaforthianum (blue or purple flowers)
Lycopersicum esculentum: It is also known as Solanum lycopersicum or tomato. It is cultivated in most parts of the world. It is an edible fruit. Tomato is also used in manufacture of sauce and ketchup.
Capsicum annum: These fruits when dried are the source of chilli powder. Chilli powder is the main spice in India. Preparations of capsicum are also used as counter irritant in lumbago, neuralgia and rheumatic disorders. The fruits of capsicum species for example Capsicum frutescence are used in making hot sauces and also it is used as a vegetable.
Physalis peruviana: It is also known as raspberry. It is cultivated for its orange-red berries enclosed in persistent bladdery calyx. The berries of Physalis alkekengi are also edible.
Nicotiana tobacum: This is cultivated as a major crop in warm countries of the world. They are cultivated for their leaves which are lightly fermented. Different varieties of tobacco are cultivated for different products like hukka, bidi, cigarette, cigar and pipe tobacco. Tobacco is also used for chewing and snuff.
It is also used in medicines as sedative, antispasmodic and vermifuge. In Agriculture it is used as insecticide and in eradication of animal pests like lice and ticks. The seeds yield semi-drying oil used in paints and varnishes. Of all the Nicotiana species, Nicotiana rustica has high nicotine content and is cultivated to a very small extent.
Atropa belladonna: The roots of this plant are the source of an alkaloid atropine. This alkaloid is the basis for the drug belladonna used in tinctures and plasters. This alkaloid possesses the property of overcoming the spasm of involuntary muscles, dilating pupils and relieving pains. This is also a valuable antidote in opium poisoning.
In India, the commercial source of belladonna is Atropa accuminata Royle also known as Indian belladonna.
Hyoscyamus niger: The dried leaves and the flower tops of this plant constitute the drug henbane. Henbane has commercial value and is used as sedative in conditions like asthma and whooping cough.
Mandragora autumnalis: The roots of these plants are used as sedative and Hypnotic agent.
Datura stramonium: The dried leaves and flower tops of this plant are the source of the drug stramonium. This drug is chiefly used to relieve the spasm of the bronchioles in asthma and in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. It is also used as the source of alkaloid atropine.
The fruit is applied to the hair of get rid of dandruff and stop hair fall. This plant is one of the important ingredients in ayurvedic reparations. Also it is important to note that the seeds of this plant are very poisonous and are employed in suicidal purposes.
Withania coagulans: The fruits of this plant are use in the treatment of asthma, chronic liver complaints, colic and blood purifier.
Withania somnifera: The roots of this plant are used in ayurvedic preparations for the treatment of hiccups, female disorders, cough and rheumatism.
The following is the list of genera belonging to solanaceae which are used for ornamental purposes
| Plant genera | Speciality |
|---|---|
| Petunia sps. | Annular plants with funnel-form flowers in shades of white, pink or purple |
| Salpiglossis sps. | Annular plants with long pedicillate flowers in various colours |
| Schizanthus sps. | Herbaceous plants with variously coloured flowers in terminal cymes |
| Nicotiana sps. | Annular plants with salver-form fragrant flowers |
| Solanum sps. | Climbers with fragrant flowers in shades of white, violet or blue |
| Brunfelsia sps | Shrubs with showy fragrant flowers in large terminal cymes |
| Cestrum sps. | Shrubs with green, whitish or yellow sweet fragrant flowers |
- Share with your friends! -
Login to post your comment here...
- or with social Account -