The cell cycle follows a remarkable timing mechanism. Most of the eukaryotic cells live according to an internal clock. They proceed through a sequence of phases called cell cycle. During the cell cycle DNA is duplicated at the synthesis phase and the resulting copies are distributed to the daughter cells during mitotic phase. Most growing plant and animal cells take 10-20 hours to double in number.
A multi cellular organism usually starts its life as a single cell zygote. And it is because of the cell cycle that this single cell grows and develops into an organism. On the other hand, unicellular organisms like bacteria and protozoans reproduce asexually through amitosis.
Cell division is a complex process by which cellular material is equally distributed between daughter cells.
Cell division in living organisms is of three types namely,
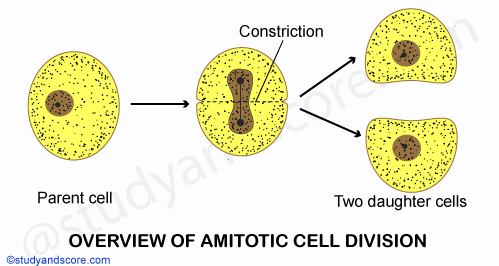
It is also known as binary fission or direct cell division. In amitosis, a somatic cell is division into two parts, each of which can grow into new complete organism. During amitosis, the nucleus elongates to assume dumb-bell-shape.
The constriction gradually increases in size and ultimately divides the nucleus into two nuclei. The division of nucleus is followed by the constriction of cytoplasm which divides the cell into two approximately similar halves. Consequently, without the occurrence of any nuclear events two daughter cells are formed.
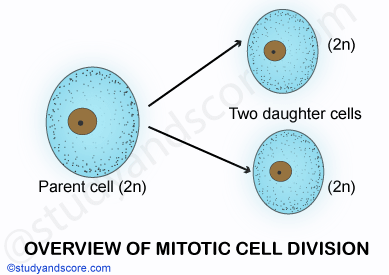
It is also known as equational cell division. It produces two daughter cells which are genetically identical. This cell division occurs in the somatic cells mainly for multiplication of cell number during embryogenesis and blastogenesis of both plants and animals. Basically, it is related to growth of an individual from zygote to adult stage.
It is also known as reduction cell division. It produces four haploid daughter cells from diploid parents. In the process, each of daughter cells has half chromosome of the parental cells. The meiotic division is of extreme importance for those organisms in which the union of the haploid gametes takes place during the sexual reproduction.
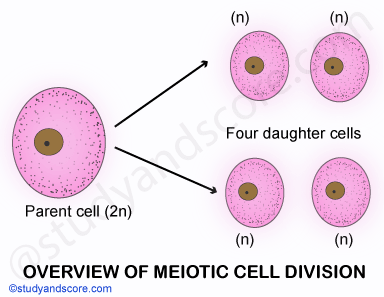
As the number of chromosomes is reduced (diploid germ cells into the haploid gametes) meiosis maintains a constant number of the chromosomes. Thus, meiosis helps in alternation of generation of haploidic generations of plants and animals. In the process of meiosis, the chromosomes divide once and but the nucleus and cytoplasm divide twice.
- Share with your friends! -
Login to post your comment here...
- or with social Account -