The term Mitosis is derived from Greek word ‘mitos’ which means thread. Mitosis occurs in the somatic cells and it is meant for the multiplication of cell number during embryogenesis and blastogenesis of plants and animals. Basically, it is related with the growth of an individual from zygote to adult stage.
One of the basic characteristics of mitotic cell division is that it gives rise to two daughter cells, which resemble each other and also the parent cell both qualitatively and quantitatively. In other words, the chromosome number of mitotic products remains same like that of the parent cell.
Mitotic cell division was first described in animals by W. Fleming in year 1882. In the same year Strasburger described mitosis in plants. In plants, active mitotic cell division takes place in apices whereas in higher animals mitotic cell division is said to be diffused and distributed throughout the body.
Mitotic cell division can be mainly distinguished into two phases namely Interphase and mitotic phase.
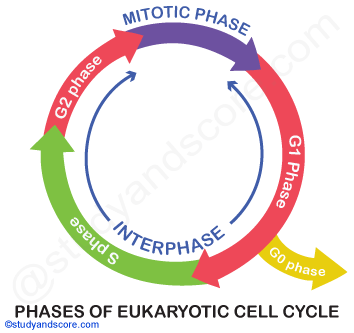
Interphase: It occupies about 90% of the cell cycle and is a period of synthesis and growth, during which the cell roughly doubles in mass but without displaying obvious morphological changes. Interphase is subdivided into
* G1 phase
* S phase
* G2 phase
Mitotic phase: It occupies the remaining 10% of the cell cycle. Once interphase is complete, the cell enters into mitotic phase. It is a brief period of intense structural changes. Mitotic phase is subdivided into
* Prophase
* Metaphase
* Anaphase
* Telophase
* Cytokinesis
The term interphase is derived from Latin word ‘inter’ which means ‘between’ and Greek word ‘phasis’ which means ‘appearance’. It occupies about 90% of the cell cycle and is a period of synthesis and growth, during which the cell roughly doubles in mass but without displaying obvious morphological changes.
Interphase as the name suggests, is the stage between two successive cell divisions during which the cell prepares itself for the process by growing in size and synthesizing new nucleic acids & proteins. Chromosomes appear as thread-like chromatin network.
Interphase consists of the following three sub stages.
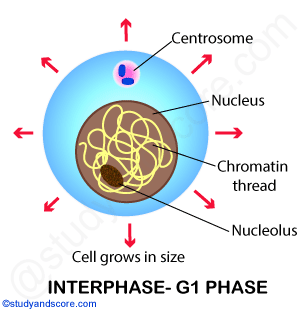
G1 or Gap-1 phase: This phase starts immediately after previous cell division. The cell grows in size and there is synthesis of new proteins and RNA which are needed for various metabolic activities of the cell. A non-dividing cell does not proceed beyond G1 phase and is said to be in G0 stage or cease phase.
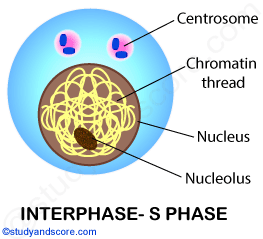
S-or Synthetic Phase: During this phase there is synthesis of DNA. And each chromosome is now composed of two sister chromatids.
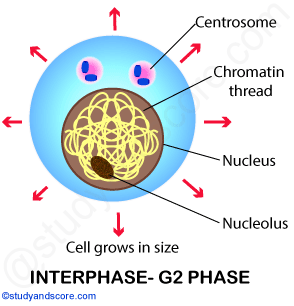
G2 or Gap-2 Phase: During this phase there is synthesis of proteins responsible for the formation of spindle fibres. Also the cell grows further in size.
In summary the following are the events which take place during interphase

- Share with your friends! -
Login to post your comment here...
- or with social Account -