Vitamin B2 was discovered in 1922, and its active ingredient was isolated in 1933 by Richard Kuhn and Wagner-Jauregg. They discovered the fluorescent green yellow substance in an effort to find a substance to stop the disease pellagra. Its scientific name originates from the word ‘flavus’ which means the color yellow in Latin.
Vitamin B2 also known as riboflavin is the only vitamin that gives you a visual indication as to its passage through your body. In other words, when there is a lot of vitamin B2 in the diet, the urine turns bright yellow to show its presence. It has also recently been found to affect the metabolism of iron in important ways. The World's Healthiest Foods are generally very rich in vitamin B2.
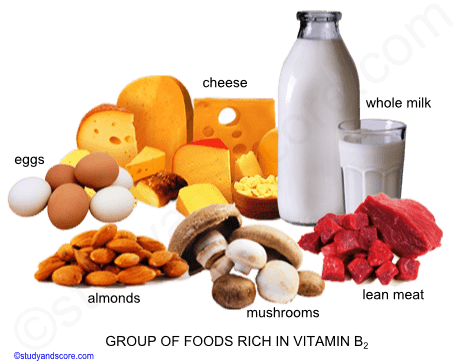
About half of the intake of riboflavin daily is furnished by milk alone and cheese is a good source. Other sources include mushrooms, Almonds, Leafy vegetables, Lean meat and eggs.
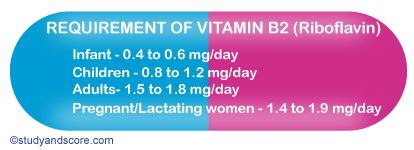
The requirement of riboflavin depends on normalization activity of the red cell enzyme (glutathione reductase) which is a flavoprotein. Its activity is sensitive to riboflavin nutritional status. The following is the requirement of riboflavin,
The vitamin is phosphorylated in the intestinal mucosa during absorption. It is absorbed from the small intestine through the portal vein and is passed to all tissues being stored in the body. The major part is excreted in urine and a small part is metabolized in the body.
Riboflavin deficiency leads to Cheilosis, a cracking of the skin at the corners of the lips and scaliness of the skin around the ears and nose. There may be redness and burning as well as itching of the eyes, and extreme sensitivity to strong light.
The following are the functions of Vitamin B2
- Share with your friends! -
Login to post your comment here...
- or with social Account -