If the entire leaf or a part of leaf undergoes permanent change to perform new functions suitable for the environment, it is called leaf modification. The leaf modifications are of the following types.
Tendrils
In weak stemmed plants, the entire leaf or any part of it modify into tendrils. They provide mechanical support to the plant and also help in climbing. Tendril is a long, wiry, slender, sensitive structure which coils round the support. Tendrils formed from the leaf are called leaf tendrils.
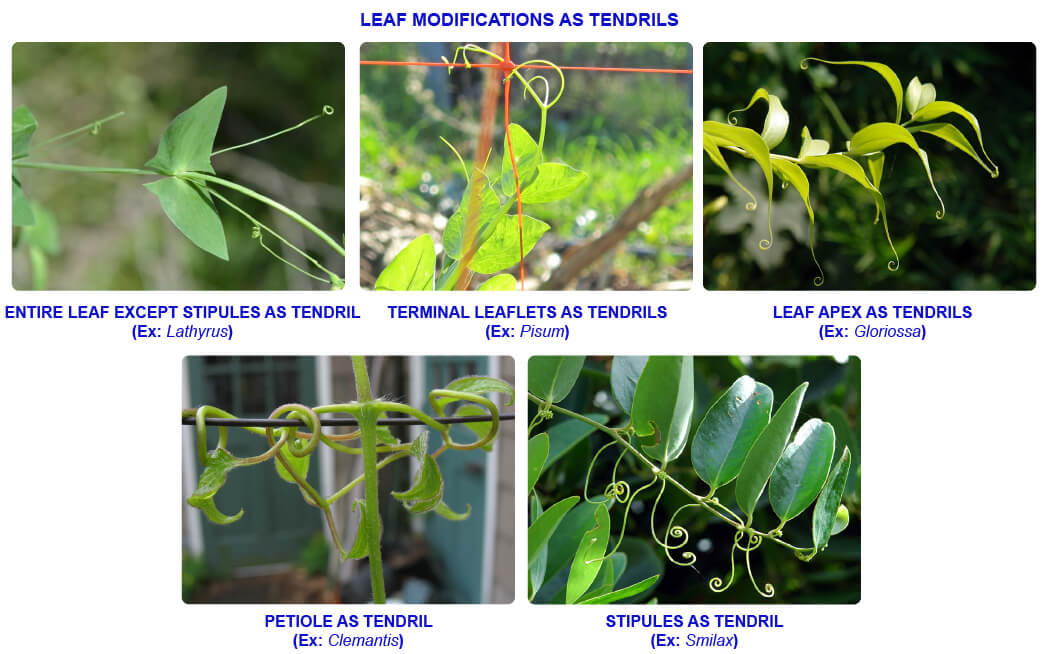
| Part of leaf modified into tendril | Plant |
|---|---|
| Complete leaf except stipules | Lathyrus (Wild pea) |
| Terminal leaflets of compound leaf | Pisum (Garden pea) |
| Leaf apex | Gloriosa superba (Glory lily) |
| Stipules | Smilax (Sarasaparilla) |
| Petiole | Clematis |
| Upper part of petiole | Nepenthes (Pitcher plant) |
Spines
In some plants leaves are modified into sharp, pointed spines. They help in reducing the rate of transpiration in xerophytic plants and also protect the plants from herbivorous animals.
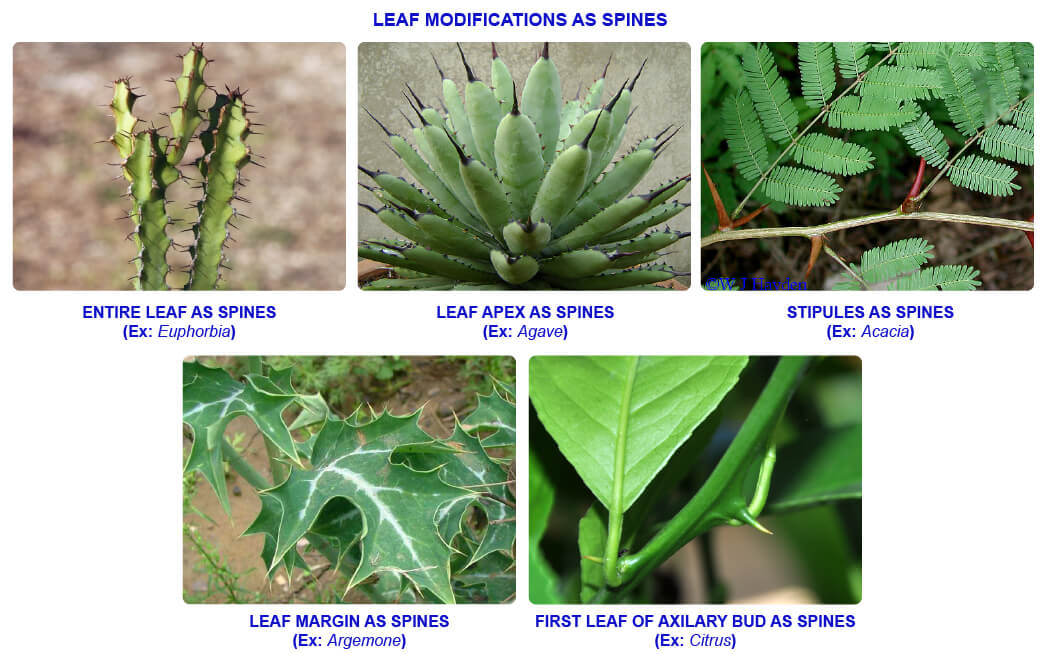

| Part of leaf modified into spine | Plant |
|---|---|
| Entire leaf | Euphorbia, Asparagus, Opuntia |
| Leaf apex | Agave, Yucca, Aloe |
| Stipules | Acacia, Ziyphus, Parkinsonia |
| Leaf margin | Argemone |
| First leaf of axillary bud | Citrus |
Scale leaves
In some xerophytic plants and in underground stems the leaves are reduced to small, colourless, dry membraneous structures called 'scales'. In desert plants these scale leaves are present on phylloclades reduce the transpiration. In underground stems they protect the axillary and terminal buds.
Example: Casuarina, Zingiber and Allium.

Phyllode
When petiole or secondary rachis is modified into green flattened winged structure performing photosynthesis it is called a phyllode.
Example: Acacia melanoxylon Parkinsonia.

In Acacia melanoxylon, the petiole is modified into a phyllode. In this, the normal leaf which is bipinnately compound develops in the seedling stage but it soon falls off. The phyllode then performs photosynthesis.
In Parkinsonia, the primary rachis and stipules modify into spines while the secondary rachii are modified into phyllodes. The small leaflets formed on this phyllode fall off soon. The phyllode then performs photosynthesis.
Reproductive leaves
In some plants leaves produce buds called epiphyllous buds and help in vegetative propagation. These leaves are called reproductive leaves.
Example: Bryophyllum, Scilla and Begonia.
In Bryophyllum, the buds lie in the notches present in the crenate margins of the leaf. In Scilla indica (squill) the buds arise from the tip of the Leaf. In Begonia, the buds arise from injured parts of leaf.

Trap leaves or Insectivorous leaves or Carnivorous leaves
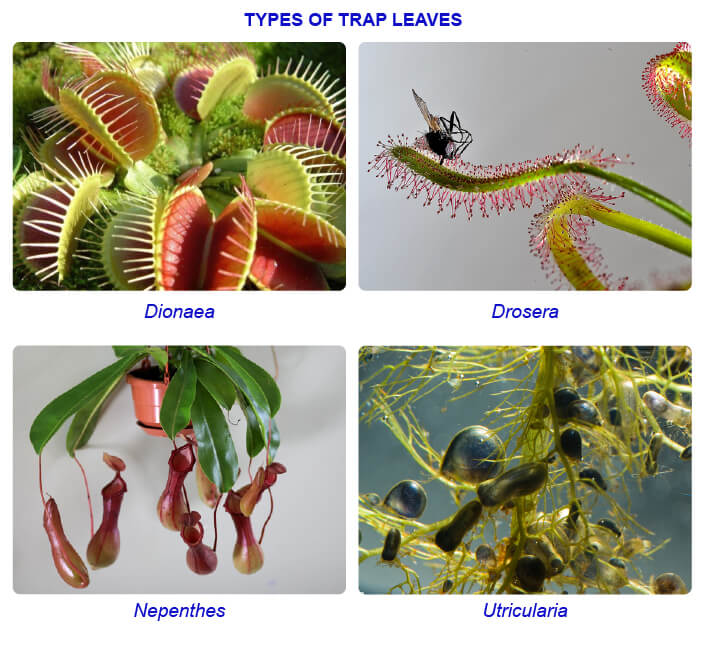
Plants growing in nitrogen deficient soils depend on organisms like insects for their nitrogen requirements. In order to attract the insects catch them and digest the insect proteins, leaves of these plants modify into trap leaves So these plants are called 'insectivorous plants'. Digestive glands are formed in these leaves which secrete digestive juices. With the help of these juices the insect proteins are digested and the nitrogenous compounds are assimilated into the plant.
Example: Nepenthes, Drosera, Utricularia and Dionaea.
Nepenthes is an insectivorous plant distributed in Assam forests. It is commonly called "pitcher plant'.
| Part of leaf modified in Nepenthes | Modification |
|---|---|
| Lower part of the petiole | Wing like structure |
| Upper part of the petiole | Tendril |
| Leaf lamina | Pitcher |
| Leaf tip | Lid of the pitcher |
The lid of the pitcher is attractive colourful and immovable. The rim of the pitcher is lined nectar glands. The upper part of the pitcher, on the inner side has laige number of digestive glands and downwardly projecting hairs. Below this is slippery surface. The hairs prevent the insect to escape out of the pitcher. The bottom of the pitcher is filled with a watery fluid which is acidic in reaction due to the secretions from the glands of the pitcher.
The insect is attracted by the colour of the lid and the sweet secretions of the nectar glands. When the insect lands on the pitcher, it slips downwards and is drowned in the acidic fluid of the pitcher: The hairs do not allow the insect to crawl in an upward direction. The insect is killed and digested by the action of proteolytic enzymes produced by digestive glands. The digested nitrogenous substances then absorbed and transported to the plant.

Difference between Phylloclade and Phyllode
| Phylloclade | Phyllode |
|---|---|
| It is the modification of an aerial stem | It is the modification of either petiole or secondary rachis |
| It has nodes, buds and flowers | It does not have nodes buds and flowers, |
| Modified leaves are present in the of spines or scales | It does not have spines or scales, as it is modification of either petiole or secondary rachis |
| Example: Opuntia, Casuarina |
Example: Acacia melanoxylon, Parkinsonia |
Difference between Thorns and Spines
| Thorns |
Spines |
|---|---|
| Thorn is a stem modification | Spine is a leaf modification |
| Thorns may bear flowers and leaves on them |
Spines do not bear flowers and leaves on them |
| Thorns may arise in the axil of leaves in place of a bud | Spines occupy the same position as the leaves and bear a bud in their axil. |
| They act as defensive structures and also serve as climbing organs of the plant | They act as defensive structures. They also help to check the rate of transpiration |
| Example: Bougarnviliea, Carissa |
Example: Opuntia |
Hope you have liked this post.
Please share it with your friends through below links.
All the very best from Team Studyandscore
“Study well, Score more…”
- Share with your friends! -
Login to post your comment here...
- or with social Account -