- We see a huge variety of clothes around us. Different clothes like bed sheets, blankets, curtains, tablecloths, towels and dusters are made of different materials.
- Clothes are made from different material depending on the use of the cloth. Some of the cloths are seasonal. For example we were cotton clothes during summer season because they keep our body cool and we wear woolen clothes during winter season as they keep our body warm.
Variety of fabrics
- If we visit a nearby cloth shop or a tailoring shop, we can touch and feel textures of various varieties of fabric pieces.
- These different varieties of fabric are made from different materials.
- Though the fabric appears to be a continuous piece, when we observe it closely we can see that it is made up of hundreds and thousands of yarns arranged together in an orderly fashion.
- Take a piece of cotton fabric, try to find a loose yarn at one of its ends and pull it out with a pin or needle.
Fibre and its types
- When we press one end of this piece of yarn with thumb finger and scratch the other end with nail, the yarn separates out into thin strands.
- The thin strands of thread that we see are made up of still thinner strands called fibres.
- Therefore, fabrics are made up of yarns and yarns are further made up of fibres.
- During ancient times, natural fibres were the only ones available for making fabrics. But, since last hundred years or so, fibres are also made from chemical substances. Hence there are two types of fibres namely artificial fibres and natural fibres.
- Artificial fibres: The fibers which are made from chemical substances are called as artificial fibres. These are also called synthetic fibres. Some examples of synthetic fibres are polyester, nylon and acrylic.
- Natural fibres: The fibres obtained from plants and animals are called as natural fibres. For example cotton, jute, silk and wool
- Cotton and jute fibres are obtained from plants. Cotton is obtained from cotton plant (Gossypium) and jute is obtained from jute plant (Corchorus)
- Wool and silk fibres are obtained from animals. Wool is obtained from the fleece of sheep and goat. It is also obtained from the hair of rabbits, yak and camels. Silk fibre is drawn from the cocoon of silkworm.
Cotton:
- Cotton is used for making wicks for diyas, filling mattresses, quilts or pillows.
- Cotton grows in cotton fields on cotton plants.
- Cotton plants are usually grown at places having black soil and warm climate.
- In our country cotton grows in Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Haryana, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Punjab, Tamil Nadu and Odisha.
- The fruits of the cotton plant are called cotton bolls.
- Cotton bolls are about the size of a lemon.
- After maturing, the cotton bolls burst open and the seeds covered with cotton fibres can be seen.
- The cotton field which is ready for picking cotton just looks like a field covered with snow.
- From these bolls, cotton is hand-picked.
- Fibres are then separated from the seeds by combing.
- This process is called ginning of cotton.
- Ginning was traditionally done by hand.
- Nowadays machines are also used for ginning.

Jute:
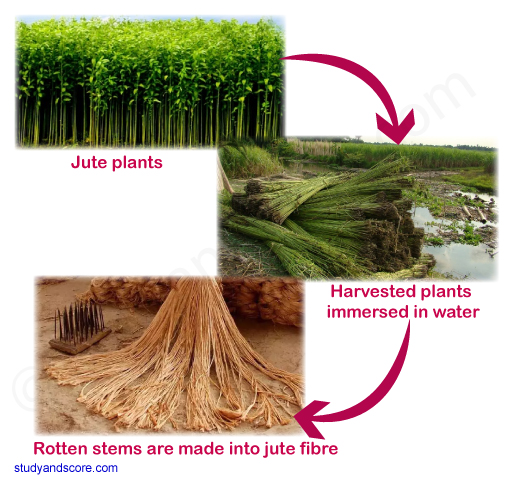
- Jute is used for making bags, ropes, mats etc. Jute grows on jute plants.
- Jute fibre is obtained from the stem of the jute plant.
- It is cultivated during the rainy season.
- In India, jute is mainly grown in West Bengal, Bihar and Assam.
- The jute plant is normally harvested when it is at flowering stage.
- The stems of the harvested plants are immersed in water for a few days.
- The stems rot and fibres are separated by hand.
- To make fabrics, all these fibres are first converted into yarns.
Spinning cotton yarn
-
Hold some cotton wool in one hand. Pinch some cotton between the thumb and forefinger of the other hand. Now, gently start pulling out the cotton, while continuously twisting the fibres. The process of making yarn from fibres is called spinning.
-
In this process, fibres from a mass of cotton wool are drawn out and twisted. This brings the fibres together to form a yarn.
-
A simple device used for spinning is a hand spindle, also called takli. Another hand operated device used for spinning is charkha.

-
Use of charkha was popularized by Mahatma Gandhi as part of the Independence movement. He encouraged people to wear clothes made of homespun yarn and shun imported cloth made in the mills of Britain.
-
Spinning of yarn on a large scale is done with the help of spinning machines. After spinning, yarns are used for making fabrics.
Yarn to fabric
There are many ways by which fabrics are made from yarns. The two main processes are weaving and knitting.
Weaving: a fabric is made up of two sets of yarns arranged together. The process of arranging two sets of yarns together to make a fabric is called weaving. Weaving of fabric is done on looms. The looms are either hand operated or power operated.
Knitting: In knitting, a single yarn is used to make a piece of fabric. Socks and many other clothing items are made of knitted fabrics. Knitting is done by hand and also on machines.
Weaving and knitting are used for making different kinds of fabric. These fabrics are used for a variety of clothing items.
History of clothing material
- During ancient times people used the bark and big leaves of trees or animal skins and furs to cover themselves.
- After people began to settle in agricultural communities, they learnt to weave twigs and grass into mats and baskets.
- Vines, animal fleece or hair were twisted together into long strands. These were woven into fabrics.
- The early Indians wore fabrics made out of cotton that grew in the regions near the river Ganga. Flax is also a plant that gives natural fibres.
- In ancient Egypt, cotton as well as flax were cultivated near the river Nile and were used for making fabrics.
- In those days, stitching was not known. People simply draped the fabrics around different parts of their body.
- Many different ways of draping fabrics were used.
- With the invention of the sewing needle, people started stitching fabrics to make clothes.
- Stitched clothes have gone through many variations since this invention. It is amazing to note that even today sari, dhoti, lungi or turbans are used as un-stitched piece of fabric.
Link to Solutions on this topic
Hope you have liked this post.
Please share it with your friends through below links.
All the very best from Team Studyandscore
“Study well, Score more…”
- Share with your friends! -



Login to post your comment here...
- or with social Account -